Virtual DOM到底有什麼迷人之處?如何搭建一款迷你版Virtual DOM庫?
為什麼使用Virtual DOM
- 手動操作DOM比較麻煩。還需要考慮瀏覽器兼容性問題,雖然有JQuery等庫簡化DOM操作,但是隨著項目的複雜DOM操作複雜提升。
- 為了簡化DOM的複雜操作於是出現了各種MVVM框架,MVVM框架解決了視圖和狀態的同步問題
- 為了簡化視圖的操作我們可以使用模板引擎,但是模板引擎沒有解決跟踪狀態變化的問題,於是Virtual DOM出現了
- Virtual DOM的好處是當狀態改變時不需要立即更新DOM,只需要創建一個虛擬樹來描述DOM,Virtual DOM內部將弄清楚如何有效的更新DOM(利用Diff算法實現)。
Virtual DOM的特性
- Virtual DOM可以維護程序的狀態,跟踪上一次的狀態。
- 通過比較前後兩次的狀態差異更新真實DOM。
實現一個基礎的Virtual DOM庫
我們可以仿照snabbdom庫
首先,我們創建一個index.html文件,寫一下我們需要展示的內容,內容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html><htmllang="en"><head><metacharset="UTF-8"><metahttp-equiv="X-UA-Compatible"content="IE=edge"><metaname="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>vdom</title><style>.main{color:#00008b;}.main1{font-weight:bold;}</style></head><body><divid="app"></div><scriptsrc="./vdom.js"></script><script>functionrender(){returnh('div',{style:useObjStr({'color':'#ccc','font-size':'20px'})},[h('div',{},[h('span',{onClick:()=>{alert('1');}},'文本'),h('a',{href:'https://www.baidu.com',class:'main main1'},'點擊')]),])}// 頁面改變functionrender1(){returnh('div',{style:useStyleStr({'color':'#ccc','font-size':'20px'})},[h('div',{},[h('span',{onClick:()=>{alert('1');}},'文本改變了')]),])}// 首次加載mountNode(render,'#app');// 狀態改變setTimeout(()=>{mountNode(render1,'#app');},3000)</script></body></html>我們在接著我們引入了一個vdom.js文件,這個文件就是我們將要實現的迷你版Virtual DOM庫。最後,我們在調用h還有,你可能會注意到在
思路理清楚了,展示頁面的代碼也寫完了。下面我們將重點看下
第一步
我們看到index.html文件中首先需要調用
// Mount node // Mount node function mountNode ( render , selector ) { }
接著,我們會看到
那麼,我們接著在vdom.js文件中再定義一個h方法。
functionh(tag,props,children){return{tag,props,children};}還沒有結束,我們需要根據傳入的三個參數
我們需要這樣操作。我們在
// Mount node // Mount node function mountNode(render, selector) { mount(render(), document.querySelector(selector)) } function mountNode(render, selector) { // Mount node function mountNode(render, selector) { mount(render(), document.querySelector(selector)) } mount(render(), document.querySelector(selector)) // Mount node function mountNode(render, selector) { mount(render(), document.querySelector(selector)) }
接著,我們定義一個
functionmount(vnode,container){constel=document.createElement(vnode.tag);vnode.el=el;// propsif(vnode.props){for(constkeyinvnode.props){if(key.startsWith('on')){el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(),vnode.props[key],{passive:true})}else{el.setAttribute(key,vnode.props[key]);}}}if(vnode.children){if(typeofvnode.children==="string"){el.textContent=vnode.children;}else{vnode.children.forEach(child=>{mount(child,el);});}}container.appendChild(el);}第一個參數是調用傳進來的
我們看到先是判斷屬性,如果屬性字段開頭含有否則,直接利用
接著,再判斷子節點,如果是字符串,我們直接將字符串賦給文本節點。否則就是節點,我們就遞歸調用
最後,我們將使用
頁面正常顯示。

第二步
我們知道Virtual DOM有以下兩個特性:
- Virtual DOM可以維護程序的狀態,跟踪上一次的狀態。
- 通過比較前後兩次的狀態差異更新真實DOM。
這就利用到了我們之前提到的diff算法。
我們首先定義一個patch方法。因為要對比前後狀態的差異,所以第一個參數是舊節點,第二個參數是新節點。
functionpatch(n1,n2){}下面,我們還需要做一件事,那就是完善是因為當狀態改變時,只更新狀態改變的DOM,也就是我們所說的差異更新。這時就需要配合
相比之前,我們加上了對是否掛載節點進行了判斷。如果沒有掛載的話,就直接調用否則,調用
let let isMounted = false ; let oldTree ; // Mount node function mountNode ( render , selector ) { if ( ! isMounted ) { mount ( oldTree = render (), document . querySelector ( selector )); isMounted = true ; } else { const newTree = render (); patch ( oldTree , newTree ); oldTree = newTree ; } }
那麼下面我們將主動看下
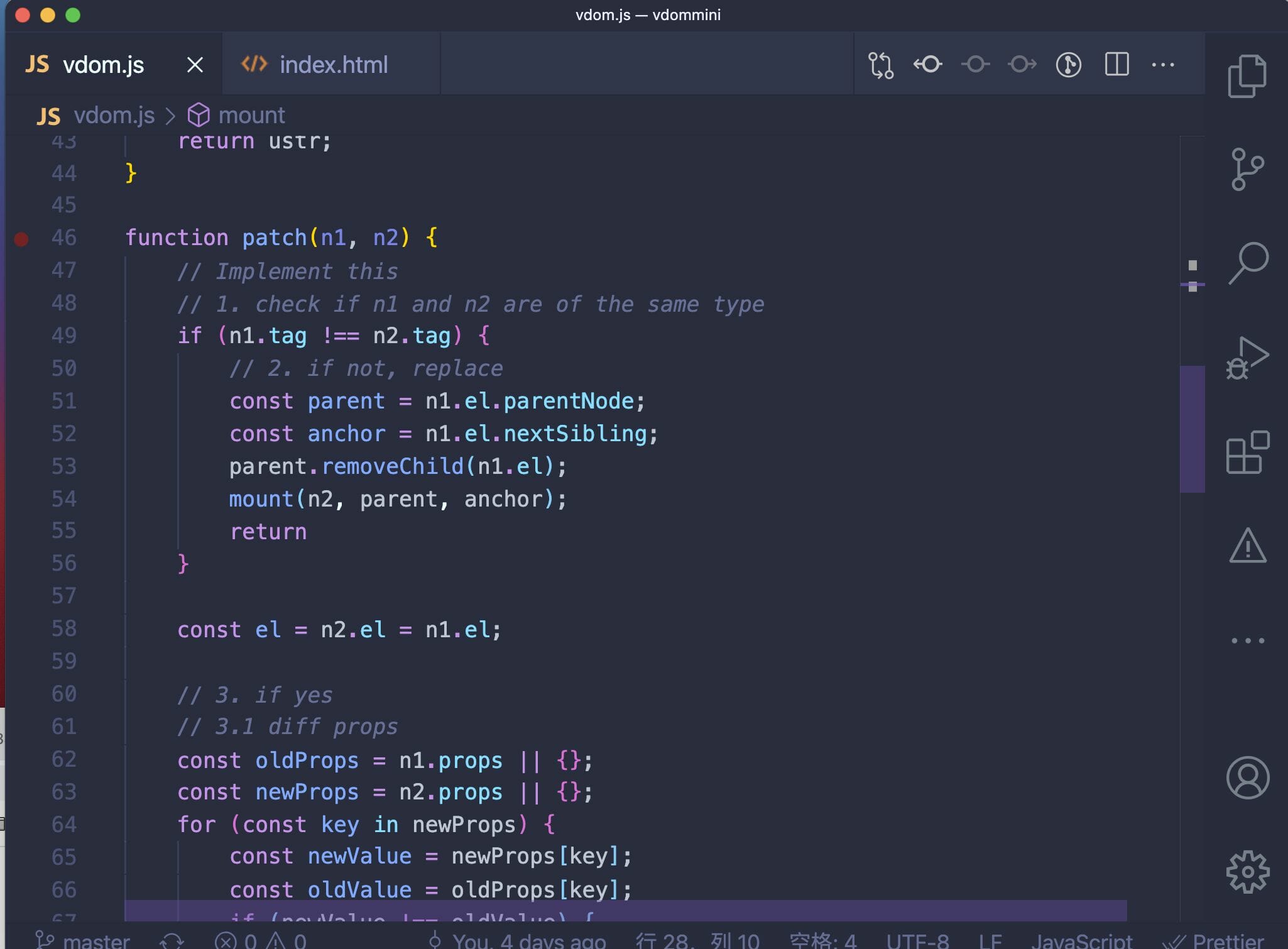
functionpatch(n1,n2){// Implement this// 1. check if n1 and n2 are of the same typeif(n1.tag!==n2.tag){// 2. if not, replaceconstparent=n1.el.parentNode;constanchor=n1.el.nextSibling;parent.removeChild(n1.el);mount(n2,parent,anchor);return}constel=n2.el=n1.el;// 3. if yes// 3.1 diff propsconstoldProps=n1.props||{};constnewProps=n2.props||{};for(constkeyinnewProps){constnewValue=newProps[key];constoldValue=oldProps[key];if(newValue!==oldValue){if(newValue!=null){el.setAttribute(key,newValue);}else{el.removeAttribute(key);}}}for(constkeyinoldProps){if(!(keyinnewProps)){el.removeAttribute(key);}}// 3.2 diff childrenconstoc=n1.children;constnc=n2.children;if(typeofnc==='string'){if(nc!==oc){el.textContent=nc;}}elseif(Array.isArray(nc)){if(Array.isArray(oc)){// array diffconstcommonLength=Math.min(oc.length,nc.length);for(leti=0;i<commonLength;i++){patch(oc[i],nc[i]);}if(nc.length>oc.length){nc.slice(oc.length).forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}elseif(oc.length>nc.length){oc.slice(nc.length).forEach(c=>{el.removeChild(c.el);})}}else{el.innerHTML='';nc.forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}}}我們從
如果新舊節點的標籤不相等,就移除舊節點。另外,利用然後,傳給這時你可能會有疑問,對,但是這裡我們需要傳進去第三個參數,主要是為了對同級節點進行處理。
if if ( n1 . tag !== n2 . tag ) { // 2. if not, replace const parent = n1 . el . parentNode ; const anchor = n1 . el . nextSibling ; parent . removeChild ( n1 . el ); mount ( n2 , parent , anchor ); return }
所以,我們重新修改下我們看到我們只是加上了對
如果insertBefore
如果
functionmount(vnode,container,anchor){constel=document.createElement(vnode.tag);vnode.el=el;// propsif(vnode.props){for(constkeyinvnode.props){if(key.startsWith('on')){el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(),vnode.props[key],{passive:true})}else{el.setAttribute(key,vnode.props[key]);}}}if(vnode.children){if(typeofvnode.children==="string"){el.textContent=vnode.children;}else{vnode.children.forEach(child=>{mount(child,el);});}}if(anchor){container.insertBefore(el,anchor);}else{container.appendChild(el);}}下面,我們再回到如果新舊節點的標籤相等,我們首先要遍歷新舊節點的屬性。我們先遍歷新節點的屬性,判斷新舊節點的屬性值是否相同,如果不相同,再進行進一步處理。判斷新節點的屬性值是否為然後,遍歷舊節點的屬性,如果屬性名不在新節點屬性表中,則直接移除屬性。
分析完了對新舊節點屬性的對比,接下來,我們來分析第三個參數子節點。
首先,我們分別定義兩個變量如果新節點的
接下來,我們看到利用
elseif(Array.isArray(nc)){if(Array.isArray(oc)){// array diffconstcommonLength=Math.min(oc.length,nc.length);for(leti=0;i<commonLength;i++){patch(oc[i],nc[i]);}if(nc.length>oc.length){nc.slice(oc.length).forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}elseif(oc.length>nc.length){oc.slice(nc.length).forEach(c=>{el.removeChild(c.el);})}}else{el.innerHTML='';nc.forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}}我們看到裡面又判斷舊節點的
如果是,我們取新舊子節點數組的長度兩者的最小值。然後,我們將其循環遞歸為什麼取最小值呢?是因為如果取的是他們共有的長度。然後,每次遍歷遞歸時,判斷
如果不是,直接將節點內容清空,重新循環執行
這樣,我們搭建的迷你版Virtual DOM庫就這樣完成了。
頁面如下所示。

源碼
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html><htmllang="en"><head><metacharset="UTF-8"><metahttp-equiv="X-UA-Compatible"content="IE=edge"><metaname="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>vdom</title><style>.main{color:#00008b;}.main1{font-weight:bold;}</style></head><body><divid="app"></div><scriptsrc="./vdom.js"></script><script>functionrender(){returnh('div',{style:useObjStr({'color':'#ccc','font-size':'20px'})},[h('div',{},[h('span',{onClick:()=>{alert('1');}},'文本'),h('a',{href:'https://www.baidu.com',class:'main main1'},'點擊')]),])}// 頁面改變functionrender1(){returnh('div',{style:useStyleStr({'color':'#ccc','font-size':'20px'})},[h('div',{},[h('span',{onClick:()=>{alert('1');}},'文本改變了')]),])}// 首次加載mountNode(render,'#app');// 狀態改變setTimeout(()=>{mountNode(render1,'#app');},3000)</script></body></html>vdom.js
// vdom ---functionh(tag,props,children){return{tag,props,children};}functionmount(vnode,container,anchor){constel=document.createElement(vnode.tag);vnode.el=el;// propsif(vnode.props){for(constkeyinvnode.props){if(key.startsWith('on')){el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(),vnode.props[key],{passive:true})}else{el.setAttribute(key,vnode.props[key]);}}}if(vnode.children){if(typeofvnode.children==="string"){el.textContent=vnode.children;}else{vnode.children.forEach(child=>{mount(child,el);});}}if(anchor){container.insertBefore(el,anchor);}else{container.appendChild(el);}}// processing stringsfunctionuseStyleStr(obj){constreg=/^{|}/g;constreg1=newRegExp('"',"g");conststr=JSON.stringify(obj);constustr=str.replace(reg,'').replace(',',';').replace(reg1,'');returnustr;}functionpatch(n1,n2){// Implement this// 1. check if n1 and n2 are of the same typeif(n1.tag!==n2.tag){// 2. if not, replaceconstparent=n1.el.parentNode;constanchor=n1.el.nextSibling;parent.removeChild(n1.el);mount(n2,parent,anchor);return}constel=n2.el=n1.el;// 3. if yes// 3.1 diff propsconstoldProps=n1.props||{};constnewProps=n2.props||{};for(constkeyinnewProps){constnewValue=newProps[key];constoldValue=oldProps[key];if(newValue!==oldValue){if(newValue!=null){el.setAttribute(key,newValue);}else{el.removeAttribute(key);}}}for(constkeyinoldProps){if(!(keyinnewProps)){el.removeAttribute(key);}}// 3.2 diff childrenconstoc=n1.children;constnc=n2.children;if(typeofnc==='string'){if(nc!==oc){el.textContent=nc;}}elseif(Array.isArray(nc)){if(Array.isArray(oc)){// array diffconstcommonLength=Math.min(oc.length,nc.length);for(leti=0;i<commonLength;i++){patch(oc[i],nc[i]);}if(nc.length>oc.length){nc.slice(oc.length).forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}elseif(oc.length>nc.length){oc.slice(nc.length).forEach(c=>{el.removeChild(c.el);})}}else{el.innerHTML='';nc.forEach(c=>mount(c,el));}}}letisMounted=false;letoldTree;// Mount nodefunctionmountNode(render,selector){if(!isMounted){mount(oldTree=render(),document.querySelector(selector));isMounted=true;}else{constnewTree=render();patch(oldTree,newTree);oldTree=newTree;}}關於作者
作者:曾獲得2019年CSDN年度部落格之星,CSDN部落格訪問量已達到數百萬。掘金部落格文章多次推送到首頁,總訪問量已達到數十萬。
另外,我的公眾號:歡迎關注我的公眾號,讓我們一起在前端道路上歷劫吧! Go!